
User testing guidelines: A step-by-step guide to optimizing your testing process

Note: In this resource, “user testing” refers to the general process while UserTesting signifies our organization and platform.
Understanding your customers is the key to any successful business, to ensure that you provide them with what they want and minimize what they find frustrating or challenging. Whether it’s a physical product or a digital experience, including websites or apps, you’re more likely to meet—and exceed—customer expectations if you consider user testing throughout the ideation, development, and optimization process. That way, in every step of developing your product, you’re creating solutions and experiences that match what your customers are seeking.
The eleven steps to successful user testing
1. Define your objective
While it may be tempting, it isn’t recommended to attempt to discover all issues and potential for improvement with your product in one single study. You risk receiving general feedback—and exhausting your test participants. By assigning one objective per study, you have a better chance of receiving specific responses that can guide you towards a tailored solution.
It's crucial to align your testing objectives with your broader business goals. This alignment ensures that the insights you gain directly contribute to your strategic objectives, enhancing the impact of the testing efforts. For example, if your business goal is to increase sales on an e-commerce site, your objective could be to streamline and enhance the checkout process. This specific focus helps you pinpoint areas of friction for users and directly addresses a critical conversion point in the customer journey.
Consider asking:
- What am I trying to learn? This might include understanding why users abandon their shopping carts on an e-commerce site or why they fail to use certain features in a mobile app.
- What are the outcomes, results, or KPIs that have the greatest impact on my business outcomes? For an e-commerce platform, this could be the conversion rate or average order value. For a mobile app, key metrics could include user retention rates or daily active users.
- Can users find the information they need? This is especially relevant for content-heavy websites like news portals or educational sites, where navigation and content discovery are critical for user satisfaction.
By focusing on these specific areas (and depending on your product type and business goals), you can ensure that the testing process yields actionable insights that drive meaningful improvements.
2. Create your test
With the UserTesting platform, you have multiple options for creating a test. You can create one from scratch, with your choice of audience and test plan. Or, you can pick from our ever-growing, pre-made template library for more guidance, which can be particularly helpful if you are new to creating tests or need to ensure you're covering standard best practices.
Exploring different test designs can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your study. For instance, scenario-based tasks are instrumental in uncovering specific usability issues by simulating real-world use cases. These tasks guide users through typical interactions with your product, revealing obstacles and pain points in a context that mirrors actual usage.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a balanced test:
- Identify Critical Features: Start by listing the critical features of your product that you need feedback on. This could range from a new user sign-up process to the checkout flow on an e-commerce site.
- Develop Scenarios: For each feature, create realistic scenarios that a user might encounter. For example, if you are testing a mobile app's navigation, you might create a scenario where a user needs to find specific information starting from the home page.
- Craft Tasks: Convert these scenarios into tasks for users to complete. Ensure that tasks are clear and direct, such as "Find the product returns policy and start the return process for an item you purchased."
- Prepare Questions: Alongside each task, prepare specific questions that target the user’s experience and any difficulties they encounter. Questions should be open-ended to elicit detailed feedback, such as "What difficulties did you face during this task?"
- Test Your Test: Before finalizing your test, run it internally or with a small group of pilot users to ensure the instructions are clear and the scenarios work as expected.
By methodically setting up your test in this way, you'll ensure that it covers all of the critical features of your product comprehensively, and captures precise user feedback on specific functionalities. This structured approach will increase the effectiveness of your test, as well as helping you achieve more targeted improvements based on user input.
3. Identify the best method of getting the answers you’re seeking
UserTesting offers the choice between conducting an unmoderated test or a live conversation. While there are no hard and fast rules about which option is the better choice, you should try to pair your expected outcome with the type of study that will support your goal and needs.
For instance, unmoderated tests are logistically deadline- and budget-friendly, and flexible, and work if you need a diverse set of contributors. Meanwhile, moderated tests, or live conversations, may be more expensive but allow for lengthier interaction between you and the contributor—which means opportunities for follow-up questions.
To better understand which testing method might be best, here's a quick comparison chart:
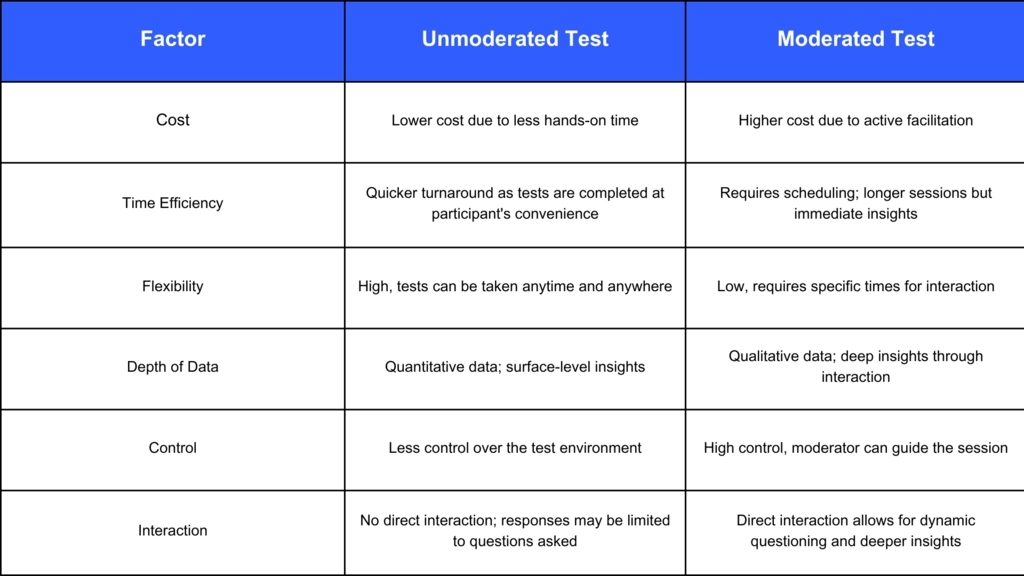
When choosing between these methods, consider factors such as:
- Budget: Moderated tests require more resources, so if cost is a constraint, unmoderated tests might be more suitable.
- Timeline: If results are needed quickly, unmoderated tests typically provide faster turnaround times.
- Nature of What’s Being Tested: If you require detailed insights into user behaviors or reactions, a moderated test can be invaluable as it allows for real-time adjustments and deeper questioning.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the testing method that best aligns with your project’s needs and goals, ensuring that you gather the most relevant and actionable data.
4. Identify what you’re studying
While your organization may have a prototype, mobile app, website, and service, you’ll receive optimal, and realistic, results if you focus on improving one product at a time. The UserTesting platform offers three product options to test: prototype, website, and app. Selecting which product—and specifically which features within that product—to test is a strategic decision that should be informed by user feedback loops, analytics, and business priorities.
Selecting product features to test:
To determine which features of your product to test, start by analyzing user interaction data and feedback. Look for patterns indicating where users experience difficulties or where engagement drops off. For example, if analytics show a high abandonment rate at the checkout page of your app, this would be a critical area to focus your testing efforts.
Utilize user feedback:
Incorporate feedback from support tickets, user forums, and reviews to identify common pain points that real users are experiencing. This direct feedback can guide you to prioritize features that need immediate attention.
Align with business priorities:
Always consider your organization’s strategic goals when deciding on features to test. If the business goal is to increase conversion rates, focus on testing and optimizing the purchase funnel. If the goal is to enhance user engagement, look at features that contribute to user retention and satisfaction.
It's easy to see how these different factors could impact success. For example, imagine an online retailer optimizing their mobile app’s checkout process based on analytics that indicated a high drop-off rate at this stage. By simplifying the form fields and adding a quick checkout option, they could potentially see a significant increase in completed purchases. Meanwhile, an educational platform that received user feedback about the complexity of navigating course content could prioritize testing its menu layout and search functionality–ideally leading to improvements in user session length and course completion rates.
By focusing on specific features that are directly linked to user feedback and business objectives, you can ensure that your testing efforts yield the most impactful results. This focused approach not only enhances the user experience but also drives your organization towards its strategic goals, demonstrating the value of targeted user testing.
5. Identify the types of people you want to include in your study
In most cases, the more diverse your participants are, the better. This could be in terms of age, gender, occupation, social networks, or more. UserTesting offers the option of building an audience from scratch or creating a link to share with those outside of the platform.
And don’t forget to think outside of the box and factor in biases. For example, you may be testing the usability of a newly updated subscription app. Instead of opting for your typical customer, consider enlisting the voices of those who previously subscribed but no longer do. This way, you can receive insight into what made them leave and what it would take for them to subscribe again.
Strategies for defining and recruiting a diverse participant pool:
- Utilize social media and professional networks: Platforms like LinkedIn, Instagram, or X can be excellent resources for reaching diverse groups. Tailor your recruitment messages to appeal to the specific demographic characteristics you need, such as specific professional expertise or consumer behaviors.
- Community engagement: Engage with online forums and communities related to your product. This not only helps in finding participants who are already interested in your niche but also in gaining deeper, more genuine insights.
And don’t forget to think outside the box and factor in biases. For example, you may be testing the usability of a newly updated subscription app. Instead of opting for your typical customer, consider enlisting the voices of those who previously subscribed but no longer do. This way, you can receive insight into what made them leave and what it would take for them to subscribe again.
Effective use of screening questionnaires:
- Balance between specificity and flexibility: While it’s important to define what you want in a contributor, being overly specific can limit your pool. Use screening questionnaires to filter participants based on essential criteria, but avoid overly narrow qualifications that exclude potentially valuable perspectives.
- Iterative refinement: Start with broader screening criteria and refine them based on the responses and the type of feedback you receive. This approach allows you to adjust your participant profile to better meet the study’s needs as you gather more information.
Remember, if you get too specific with your demographic parameters, or set up too many screeners, you may not find the unicorn contributor you’re looking for. Being definitive about what you want in a contributor, but also flexible, will bring a better payoff than checking off every box on your list for the sake of it.
6. Determine how many test participants to include
It’s been demonstrated that five participants will uncover 85 percent of the usability problems on a website and that additional users will produce diminishing returns. Resist the temptation to “boil the ocean” by doubling or tripling the number of participants in an attempt to uncover 100 percent of your usability problems. It’s easier and more efficient to:
- Run a test with five participants. This number is generally sufficient to identify the majority of significant usability issues.
- Make changes based on the feedback from these initial participants.
- Run another test with a different set of five users. This helps confirm that the changes were effective and can reveal any remaining major issues.
- Continue iterating until all major challenges are resolved.
If you’re looking for trends and insights beyond basic usability issues, it’s helpful to include a larger sample size. Here at UserTesting, five to eight participants are recommended for qualitative research. Where statistical significance and broader patterns are necessary, over 30 contributors can be enlisted for quantitative research.
By following this iterative process of testing, you can efficiently address usability problems without excessive resource expenditure, ensuring that the development of your product is both effective and economical.
7. Build your test plan (for unmoderated studies only)
If you’re creating an unmoderated test, start assembling your study by creating a test plan. Your test plan is the list of instructions that your participants will follow, the tasks they’ll complete, and the questions they’ll answer during the study.
Task and question structure:
- Broad tasks: Use these to capture a wide range of user interactions and experiences. For example, ask users to explore a new feature on your digital service broadly, noting any navigation issues or points of confusion.
- Specific tasks: These are crucial when you need detailed feedback on a particular aspect of your product. For instance, direct users to complete a purchase using a newly implemented checkout process on your e-commerce site.
Tip: Consider using both broad and specific tasks in your study. While broad tasks offer better diversity in responses, specific tasks are especially helpful when you’re seeking tailored feedback on a specific area.
Example test plan for a digital service (Website or app):
- Task: Navigate to the homepage.
- Question: Was it clear where to begin your journey? Please explain your first impression of the homepage layout.
- Task: Find and use the search feature to locate a product you're interested in.
- Question: Describe your experience with the search feature. Did it meet your expectations?
- Task: Proceed to checkout with the chosen product.
- Question: Detail any difficulties you encountered during the checkout process.
Example test plan for a physical product (Consumer electronics):
- Task: Unbox the product and set it up.
- Question: Were the instructions clear and easy to follow? Please list any issues you faced during the setup.
- Task: Use the product for a specific function, e.g., taking a picture with a camera.
- Question: Evaluate the ease of accessing and using this function.
- Task: Attempt to connect the product to another device or service.
- Question: Describe your experience with connectivity. Were there any obstacles?
Throughout these steps, you may want to sprinkle in questions on usability and whether one was able to complete tasks successfully or not. This approach ensures that your test plan not only measures the usability of your product in various contexts but also engages the participants in a manner that elicits clear, actionable feedback.
8. Launch a dry run test
Before you launch your test to all participants, we recommend conducting a dry run (sometimes called a pilot study) with just one or two participants. This will determine whether there are any flaws or confusing instructions within your original test plan.
Common pitfalls during dry runs could include:
- Unclear instructions: Participants may misunderstand tasks due to vague or overly technical language.
- Inadequate task design: Tasks may not effectively elicit the type of user interaction needed to achieve your objectives.
- Insufficient depth in questions: Initial questions may be too surface-level, failing to dig deeper into the user experience.
For instance, you may find that contributors’ test results are shorter than you expected, which could prompt you to add more detail to your task questions, or more task questions overall. Adjusting these elements based on dry run feedback ensures that the full study will be more likely to meet its goals. Otherwise you could find yourself facing situations like these (anecdotal) examples:
- Ecommerce website case: In one pilot test for an ecommerce site, the initial tasks did not effectively measure the ease of finding products. The dry run revealed that users struggled with the search functionality, which was not originally a focus of the test. Based on this, the test plan was adjusted to include specific tasks around using and evaluating the search feature, leading to significant improvements in the website's user interface.
- Mobile app case: A dry run for a mobile app intended to evaluate navigation led to discovering that testers were bypassing an important feature because it was hidden within the menu options. The feedback led to a redesign of the app’s layout to make important features more prominent and accessible.
While an extra step, taking the opportunity to make adjustments and improve the test plan before launching it fully will save you both time and budget. These adjustments ensure that when you do go to full testing, your efforts are well-directed and more likely to result in valuable insights.
9. Analyze your results
The moment you’ve been waiting for—the results are in. As you review answers to your questions, keep an eye out for similar responses and themes as well as any major deviations. If a significant number of your study participants provide similar feedback, this could signal an issue that impacts your larger customer base and deserves some attention. Or, if one or a small number of participants share a unique piece of feedback, you can hone in on this particular video to better understand why that participant or multiple participants had such a different experience.
Methodologies for analysis:
- Qualitative analysis: This involves interpreting the data to understand the underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. It includes categorizing feedback, noting language and sentiment, and identifying recurring themes or significant outliers. Using qualitative data analysis software can aid in this process by tagging and sorting responses according to predefined categories.
- Quantitative analysis: This focuses on quantifying data and applying statistical tools to decipher patterns and trends. Software tools can help track specific metrics like task completion rates, time on task, and click-through rates across different segments of users.
Using software tools for analysis:
- Utilize video analysis tools to observe user interactions and facial expressions that indicate frustration, confusion, or satisfaction. These tools can help you segment videos based on keywords or specific actions.
- Data analysis platforms can aggregate user metrics to provide a quantitative view of user behavior, enabling easier comparison and pattern recognition.
Tips on categorizing feedback and identifying patterns:
- Develop a coding system: Before diving into the data, create a set of codes that represent different types of feedback (e.g., usability issues, feature requests, navigational difficulties).
- Assign codes to feedback: As you sift through the data, assign these codes to specific pieces of feedback to help organize the data into actionable categories.
- Look for patterns: Once the data is coded, look for patterns or trends that suggest widespread issues or opportunities for improvement. This could be a particular feature that many users find difficult to use or particularly enjoyable.
Take note of user frustrations as well as things that users find particularly helpful or exciting. By knowing what people love about your product experience, you avoid the possibility of “fixing” something that’s not really broken. Hearing about things that customers struggle with, as well as enjoy, can support informed discussions on future product and experiential improvements.
10. Share your findings
After you’ve uncovered your findings, you can share them with your team and stakeholders to begin discussing the next steps. With the UserTesting platform, you can create a highlight reel that aggregates critical video clips. This is especially helpful when you have multiple participants with the same opinion—the curation of this feedback can be compelling.
Or, consider creating charts to represent interesting data and findings from your questions. This can be used to visually convey the volume of participants who say similar things (such as a word cloud) or to display the difference in opinions. In addition to videos or chats, you may even feel inclined to share participant quotations from the studies to back up your hypotheses or recommendations. Hearing straight from the voice of the customer is a powerful step in aligning team members and other stakeholders.
Expanding presentation techniques for different stakeholders:
- Visual aids for clarity: Utilize visual aids like heatmaps or flowcharts to illustrate user behaviors and issues more vividly. Heatmaps are particularly useful for showing where users click most frequently on a page, while flowcharts can demonstrate how users navigate through your app or website, pinpointing where they drop off or encounter problems.
- Customized presentations: Tailor the presentation of your findings to the interests and roles of different stakeholders. For instance, technical teams may require more in-depth analysis on specific usability issues, while marketing teams might benefit from insights into user demographics and satisfaction levels.
- Interactive presentations: Consider using interactive elements in your presentations, such as live demonstrations of the user testing videos or interactive data dashboards. This allows stakeholders to explore the data themselves and may lead to more engaged and productive discussions.
Tips for effective communication:
- Start with key insights: Begin your presentation with the most critical findings to immediately capture the attention of your stakeholders.
- Use storytelling: Frame your data within the context of user stories to help stakeholders empathize with the users and understand the practical implications of the insights.
- Recommend actions: Always connect your findings to actionable recommendations. This not only highlights the relevance of the insights but also provides a clear path forward.
By employing these enhanced presentation techniques and focusing on clarity, relevance, and engagement, you can more effectively communicate your findings and ensure that they lead to informed decision-making and strategic actions.
11. Champion a customer-focused attitude throughout your organization
Whether you’re a beginner to user testing or not, we encourage you to gather customer insights throughout your product and campaign development process, and across multiple teams and departments.
This holistic approach ensures that every facet of your organization is aligned with the needs and expectations of your customers.
Strategies for fostering a customer-focused culture:
- Regular sharing of customer insights: Make customer feedback a regular part of team meetings and company updates. This keeps everyone informed and focused on the customer experience as a core part of your business strategy.
- Training and development: Offer training sessions that help employees understand the importance of customer feedback and how it can be leveraged to improve their work. Include practical sessions on interpreting user testing data and applying it to daily tasks.
- Reward customer-centric behaviors: Recognize and reward actions and initiatives that demonstrably improve customer satisfaction. This not only motivates employees but also sets a standard for what is valued within the organization.
The earlier in your process, the better, as it’ll help you better understand customer pain points and challenges, in order to brainstorm and support product and solution ideation. You can also hone in on the right customers and audiences to assess market opportunities and analyze product-market fit. Additionally, you can understand usability challenges in your prototypes or early-stage products to course-correct before you spend too much time or resources on the development.
As you launch new digital experiences, you should monitor how customers are reacting to and interacting with these new products. This yields ideas on how to continue evolving your product.
Implementing insights across departments:
- Product development: Use user testing data to refine product designs and functionality, ensuring that development efforts are truly aligned with user needs.
- Marketing: Tailor marketing strategies based on user demographics and feedback. This can include targeting communications based on user preferences and behaviors identified through testing.
- Customer service: Train customer service teams on common issues discovered through user testing, preparing them to handle these issues effectively when they arise in real customer interactions.
Seeking frequent feedback and insights from your customers is the best way to keep your finger on the pulse of customer challenges and expectations. This ensures that you’re making the right decisions and taking all the right steps toward ongoing customer loyalty and satisfaction. By integrating customer insights into every aspect of your organization, you create a strong, customer-focused culture that drives continuous improvement and sustainable success.
Ready to take your user testing to the next level? Start creating better digital experiences today.

Want to learn more?
Bring customer perspectives into more decisions across teams and experiences to design, develop, and deliver products with more confidence and less risk.





