How to test automotive experiences
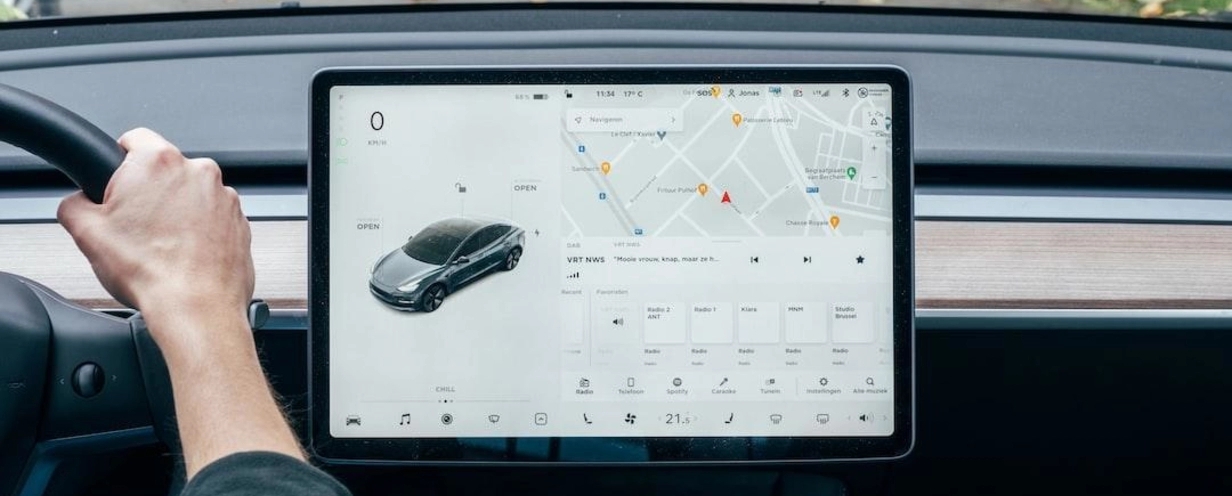
As the automotive industry continues to undergo digital transformation, user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) are becoming increasingly important. Automotive UX/UI is now integral to creating a seamless and user-friendly vehicle experience.
Today's drivers and passengers expect the same convenience and satisfaction from their vehicles' digital devices. So, creating a remarkable automotive user experience requires a fusion of aesthetics, functionality, connectivity, personalization, and ease of use.
A well-executed UX/UI strategy goes beyond impressing customers and is often a defining factor that sets a brand apart from competitors. It can influence customer loyalty and identity, redefining how people perceive their vehicles and the driving experience.
Automotive UX/UI basics
Automotive UX/UI are critical components of modern vehicle design that focus on enhancing user interaction with a car's technology and features. A well-designed UX and UI are essential as advanced technologies like infotainment systems, driver-assistance features, and connectivity options become more common in vehicles.
UX and UI in the automotive sector
UX refers to users' overall experience interacting with a vehicle's digital and physical components. It encompasses everything from the ease of navigation on a touch screen to the tactile feedback from control knobs. In automotive UX design, UX considers a user's emotions, preferences, and expectations as a driver or passenger, ensuring the vehicle's features meet or exceed those expectations.
To achieve an optimal UX, automotive UX designers focus on the following aspects:
- User needs: Understanding what the user wants and needs is essential. It may include intuitive control layouts, easy access to information, or being able to customize settings like seat adjustments.
- Accessibility and usability: Ensuring easy access and intuitive use of various features—from climate control to navigation—without unnecessary complexity or confusion is critical.
- Emotional connection: Building an emotional connection with users by creating designs that reflect quality or elegance, depending on the brand and model, is also essential.
UI is the visual and interactive part of a vehicle's system that allows the user to control and receive feedback from the various features and functions. It includes touch screens, buttons, voice commands, haptic feedback, and other interfaces enabling user and vehicle communication.
Critical components of automotive UI design include:
- Design aesthetics: From the layout of buttons to the color scheme of the display, automotive UI design focuses on providing the user with an appealing and intuitive visual experience.
- Interaction design: This considers how the user interacts with the vehicle's controls, whether through touch, voice, or physical buttons. Good UI design ensures these interactions are natural and efficient.
- Feedback and responsiveness: When the user changes a setting or inputs a command, the vehicle's system must respond promptly, confirming the user's action.
- Integration with UX: While UI is the interface users interact with, it must align with the overall UX goals, creating a cohesive and satisfying experience.
UX and UI have significantly evolved in the automotive sector, largely driven by the disruption of companies like Tesla. One of the defining moments in modern automotive design has been the realization that a user's experience starts well before they get behind the wheel. It begins with car buying and carries over into driving, maintaining, and upgrading the vehicle.
For example, in addition to design innovations, Tesla has revolutionized the traditional automotive buying experience. Tesla's direct-to-consumer model lets buyers digitally design and order cars with transparent pricing, followed by electronic documentation and flexible delivery options. Post-purchase, Tesla offers features like at-home repairs, wireless software updates, and a continuously improved driving experience. As a result, 91% of Tesla owners cite better user experience as a reason to buy a Tesla vehicle.
Importance of UX/UI in enhancing automotive products and experiences
The role of UX and UI expands far beyond mere aesthetics. Excellent UX and UI also have other positive effects that include:
- Enhancing safety: A well-designed user interface minimizes distraction and confusion. Clear, intuitive controls and displays mean the user spends less time fumbling with controls and more time focusing on the road.
- Improving usability: An effective automotive UX/UI ensures users can easily interact with the vehicle's features. Whether it's adjusting the climate control, navigating to a destination, or connecting a phone, the design aims to make these tasks as straightforward, fast, and intuitive as possible.
- Personalizing experiences: Modern automotive UX/UI enables a high level of personalization. This means the settings are customizable and that the vehicle remembers a user's preferences for seat positions, climate settings, favorite radio stations, and more.
- Enhancing brand image: Automakers use UX and UI design to project their brand's image and values. Whether aiming for a luxurious, sporty, or environmentally friendly image, the user experience design helps relay the message.
- Encouraging brand loyalty: A satisfying UX/UI leads to a better overall experience with the vehicle. This satisfaction often translates into brand loyalty, as customers are likelier to return to a brand that offers an enjoyable and intuitive driving experience.
- Facilitating new technologies: With advanced technologies like autonomous driving and driver-assistance systems becoming more commonplace, UX/UI has become critical in making these technologies accessible and understandable to users. Well-designed UX and UI bridge the user and complex automotive technologies, simplifying user interaction so that drivers can easily utilize these features.
Automotive UX/UI challenges
Automotive user experience and interface designers have to tackle several unique challenges. These range from the increasing complexity of vehicle interfaces to ensuring seamless usability for various users in different scenarios and countries.
The complexity of digital interfaces in modern vehicles
Today's vehicles are essentially computers on wheels. The digital interfaces of modern vehicles integrate multiple functions ranging from navigation to music control and vehicle settings or preferences.
This extensive functionality translates into complexity, which increases the challenge of designing swift and easy user interactions. Designing an intuitive interface that accommodates all these features without overwhelming the driver or taking too much attention off the road is an important concern in automotive UX/UI.
Ensuring safety and usability while minimizing driver distraction
Striking a balance between functionality, usability, and safety is a significant challenge in automotive UX and UI design. Today's drivers demand high-tech features that increase convenience.
For example, touch screens have become a common feature in modern vehicles. While they offer a wide range of controls and information at the driver's fingertips, interacting with touch screens is visually and mentally demanding. Drivers may need to take their eyes off the road for an extended period to locate and tap the desired function on the screen, leading to increased distraction and potential safety risks.
To address these challenges, automotive UI designers must ensure these tech enhancements translate into minimally distracting and safety-optimized driver experiences. This involves carefully designing the layout, placement, and interactions of on-screen elements to minimize the driver's cognitive and visual load. Elements such as buttons, menus, and information displays must be easily accessible and quickly understandable.
The use of haptic feedback, voice commands, and steering wheel-mounted controls can also help reduce distraction. They provide tactile and intuitive ways for drivers to interact with the vehicle's features without taking their hands off the steering wheel or their eyes off the road.
Varying user contexts
Unlike consumer electronics, in-car interfaces must account for diverse usage contexts. The optimal UX in a rainy, nighttime driving scenario will differ considerably from daytime city driving. For example, nighttime highway driving requires alertness, while traffic jams demand distraction mitigation. Also, the same user may want different information while driving leisurely versus rushing to work.
Crafting an interface adaptable to many combinations of external and internal variables is an immense challenge. These variables include lighting, weather, terrain, number of passengers, driver state, trip purpose, vehicle speed, and road type. Extensive testing across representative contexts is vital to create truly adaptive automotive UX.
Limited screen real estate
Limited screen real estate in vehicles is another significant challenge. The confined space within vehicle displays restricts how much information can be presented to the user.
This limitation demands a careful selection and prioritization of essential elements. Designers must skillfully integrate all features and controls while ensuring the displays are uncluttered and easily understood at a glance.
Ease of use for non-technical users
Modern vehicles often contain complex technologies, while drivers and passengers may have varied technical expertise. The challenge lies in making these complex systems accessible without compromising essential features through excessive simplification. Oftentimes, designers face “give-and-take” scenarios.
For example, while designing a smart navigation system, the decision to exclude advanced route planning options to simplify the interface could compromise the overall driving experience for more tech-savvy users who appreciate sophisticated features.
Automotive UX/UI designers must also account for the diversity of users’ ages. Different age groups, from young drivers to older individuals, have unique needs and preferences regarding user interfaces. Designers must ensure the interface is intuitive and easy for individuals of all ages and technical backgrounds to use.
Moreover, car brands have a global reach, with vehicles used in different countries with various languages and cultural norms. Designing for international audiences requires careful consideration of language localization, cultural sensitivities, and ensuring that the interface is accessible to users worldwide.
Addressing automotive UX problems effectively requires a deep understanding of the diverse user base's needs and expectations while ensuring the interface isn't overwhelming or cumbersome. Balancing technological innovation and ease of use creates a unique challenge in automotive UX/UI design.`
Future-proofing designs
With rapid technological advancements, future-proofing UX/UI designs is an ongoing challenge. These designs need the flexibility to adapt to future developments, ranging from AI integration to fully autonomous driving.
The complexity of future-proofing lies in anticipating changes in the technological landscape and user needs many years down the line. There's a need to balance current design practices with the flexibility to adapt to future developments. This includes accommodating new software updates, hardware changes, and user behavior shifts.
Predicting these changes and building adaptability is challenging. It requires a forward-thinking approach and a deep understanding of current trends and potential future directions in technology and user experience.
Role of UX testing in addressing automotive UX/UI challenges
In the face of challenges presented by automotive UX/UI design, user testing is critical in effectively addressing these hurdles:
- Validating design concepts early: User testing helps validate ideas and concepts early in the design process. It saves significant time and resources at later stages.
- Ensuring usability and safety: Involving actual users in the testing phase provides first-hand information about how they interact with the design and helps address any usability and safety concerns.
- Optimizing for diverse user contexts: Considering the perspective of users in different age groups, tech-savviness, and driving conditions, ensures the design caters to a broad spectrum of user needs.
- Understanding user priorities: Insightful user testing aids in aligning interface design with user preferences and needs.
- Evaluating accessibility and ease of use: Through valuable insights into how diverse users navigate the interface, user testing reveals difficulties and roadblocks that may not be noticeable to UX/UI designers.
- Furnishing long-term solutions: The feedback gathered through user testing helps anticipate future trends or changes in user behavior. It's crucial for creating sustainable and future-proof designs.
Key metrics and parameters for evaluating automotive UX/UI
Assessing the effectiveness of automotive UX/UI design requires understanding and implementing specific parameters and metrics. Here's a look into some of these crucial data points.
Usability metrics
Usability is a fundamental aspect of great UX/UI design. Some key usability metrics include the following:
- Task success: Can users complete a task using the design without errors?
- Efficiency: How quickly can users complete a task?
- Learnability: How easily can users understand how to use the interface?
User satisfaction
Any user interface's ultimate goal should be high user satisfaction, which organizations can measure through user surveys and feedback. Attention to the Net Promoter Score (NPS) can be particularly beneficial. NPS helps gauge how likely a user is to recommend products to others.
Eye-tracking metrics
In the automotive sector, UX/UI designs must minimize driver distraction. Eye-tracking studies provide valuable insights into where users primarily focus their gaze and how long it takes to find certain information on the interface. This information helps optimize the interface to be more intuitive and user-friendly. In turn, it reduces driver distractions and improves overall safety.
Cognitive load
Cognitive load measures how much mental effort users need to interact with the design. For automotive UX/UI, it's crucial to keep cognitive load minimal to avoid overwhelming or distracting the driver. Task completion times and error rates provide insights into this aspect.
Comparison with benchmarks
Comparing a design's performance with industry standards or competitors' designs allows for valuable insights and benchmarking. This analysis clearly explains where the design stands in the market and highlights areas that need improvement.
Adaptability metric
This metric determines how easily the design adjusts to changing user needs and new technological developments. It helps designers better understand the required future-proofing of UX/UI design.
These metrics give clear evidence of success or areas for improvement. For example, if the metrics show drivers use a new voice navigation feature often and without problems, that's a success. But if drivers aren't using the voice feature—or if it's causing too many errors—it's a sign the design needs improvement. Such crucial insights guide interface refinement and help elevate the UX/UI to give users a superior experience.
Integrating in-car user testing with digital UX/UI research
Understanding the intricate dynamics of automotive UX/UI design requires integrating in-car user testing with digital UX/UI research. This synergy combines practical user behavior in real-world testing conditions and analytical user research through software and tools. It leads to a more complete representation of the user experience.
In-car user testing lets you observe users in a real-world context, interacting with the system during actual driving conditions. You obtain insights about usability, safety, and overall user experience by studying this natural interaction between the user and your design.
Conversely, digital automotive UX/UI research leverages various online tools and techniques to obtain quantifiable metrics, such as user task completion rates, error rates, and interaction times. It also makes gathering feedback from a larger pool of participants easier, offering a broad perspective on user performance and satisfaction.
While both these methods have unique strengths, integrating them provides significantly richer and more comprehensive insights. An integrated approach helps designers understand how real-world users interact with the UX/UI design. The invaluable insights gathered through this process help designers create automotive experiences that are exciting, innovative, intuitive, efficient, and safe for all users.

Build competitive automotive experiences with UserTesting
Building a competitive automotive experience requires carefully balancing innovation, user needs, safety considerations, and future-proofing. It's a complex web of factors where UserTesting provides an unparalleled edge.
UserTesting equips UX/UI designers with robust tools for creating intuitive, engaging, and safe automotive experiences. For example, with our platform, users can test in-car touch-screen experiences on mobile devices, allowing numerous user feedback data points to be quickly gathered. This helps designers validate design concepts early and optimize for diverse user contexts.
UserTesting also helps UX/UI designers find the right target demographic for your automotive UX/UI testing. Our platform allows for easy recruitment of participants based on various demographics, including age, location, and driving experience. Participant criteria can be customized to ensure testing is done with the specific user groups relevant to the automotive product.
In addition to in-car testing, UserTesting offers moderated interviews to gauge how users feel about their experience. This qualitative feedback provides deeper insights into user emotions, preferences, and pain points.
Integrating in-car user testing with digital UX/UI research, UserTesting offers comprehensive, real-world human insights that drive design decisions. Our platforms provide valuable data on usability metrics, user satisfaction, eye-tracking, cognitive load, and adaptability. These insights highlight how real-world users interact with the UX/UI design and guide the creation of automotive experiences that are exciting, innovative, intuitive, and safe.
Building with UserTesting is building for success—ensuring UX/UI designs stand out as competitive and compelling products in the industry.
Frequently asked questions
How would you improve the user interface of a car?
To improve a car's user interface, conduct UX research, use automotive UI design software, and focus on safety and ease of use. Collaborate with experts and utilize customer insights to build an intuitive, user-friendly design.
Do car companies use UX teams to design cars?
Car companies employ automotive UX researchers and designers to enhance user-friendly interfaces, aligning the design with driver needs and preferences.
UX/UI design: What is done first between UI and UX?
In design, UX generally precedes UI. You first define the user experience, focusing on users' needs, and then craft the visual aspects during the UI design stage

Unlock your customer insight ROI
Discover the hidden ROI of your customers' insights. Book a meeting with our Sales team today to learn more.
In this Article






